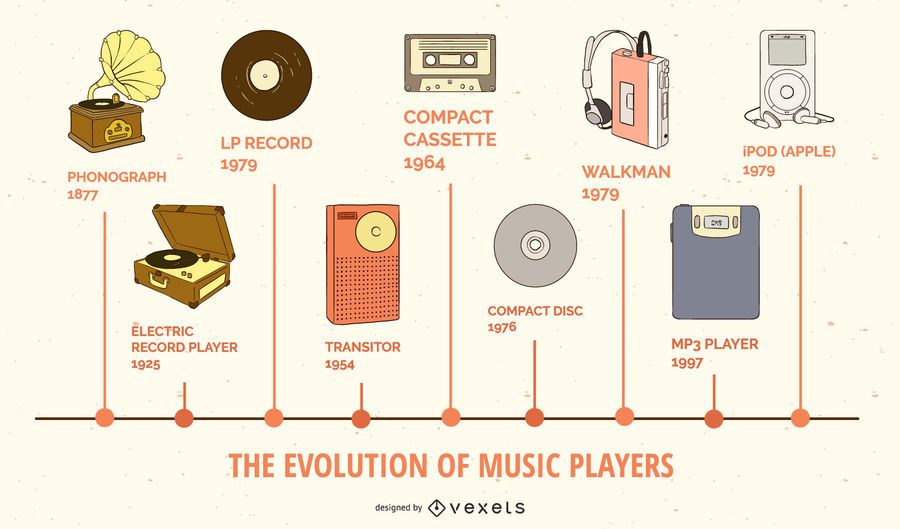
Music has always been a spiritual experience, our ancestors have made tunes out of wood and stones. It always has a soothing effect on our souls and makes us happy and forget our problems. The stepping stone of music is when we have created a realm to record and store music and play at our leisure, since then it has become a big leap for mankind.
In this article, we will learn more about the music players and their evolution in an ascending order.
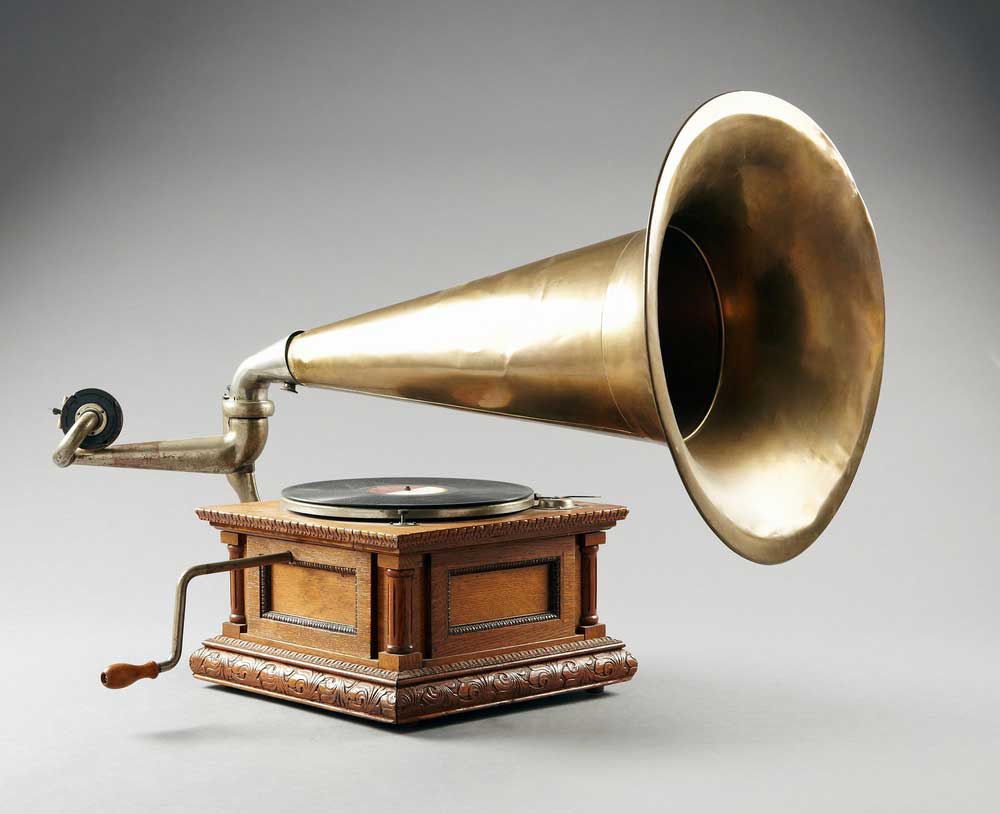

Phonogram (Late 19th Century – 1980s):
The first music player ever created in the world, known for its iconic vinyl record and distinguished sound from its oddly shaped speaker. It does not need an external power source and just works with hand winding. It works on a simple mechanism, a pin reader when it contact with the spinning vinyl record gives the sound output. Modern dj console are inspired from the vinyl player and still uses it to make the ultimate Dubstep music.
Pros:
- It does not need an external power source
- Easy to maintain
- Build like a tank and lasts forever
- Looks classy and heritage
Cons:
- Does not have a bass effect
- It’s mono sound
- Vinyl records are expensive and have a limited collection
- Expensive

The Rise of Cassette Tapes and Walkmans (1970s – 1990s)
In the 1970s, the introduction of compact cassette tapes revolutionized the music industry. Compact and portable, cassette players offered music lovers unprecedented mobility. The iconic Sony Walkman, introduced in 1979, epitomized this newfound freedom, allowing users to listen to their favorite tunes on the go. The Walkman became a cultural phenomenon, reshaping how people experienced music and influencing lifestyle trends.
Pros
- Portable and compact design, ideal for on-the-go listening.
- Rewind, fast forward, and pause functionality for user control.
- Affordable and widely accessible format for music distribution.
Cons
- Susceptible to degradation and tape warping over time.
- Limited sound quality compared to other formats.
- The inconvenience of rewinding or flipping tapes to access different tracks.

Compact Discs and the Digital Revolution (1980s – 2000s):
The 1980s witnessed another significant milestone with the introduction of compact discs (CDs). Offering superior sound quality and durability compared to vinyl records and cassette tapes, CDs quickly gained popularity among consumers. CD players became ubiquitous in homes and cars, gradually replacing older formats. The digital revolution, fueled by advancements in technology, paved the way for the development of digital audio formats such as MP3, WAV, and AAC. The emergence of CD burners and MP3 players further transformed the music landscape, empowering users to create personalized playlists and carry thousands of songs in their pockets.
Pros
- High-quality digital audio with minimal degradation.
- Durable and resistant to scratches compared to vinyl records.
- Convenient track skipping and random playback features.
Cons
- Limited storage capacity per disc.
- Vulnerable to skipping or damage due to physical movement.
- Transitioning between CDs can be cumbersome, especially in multi-disc changers.
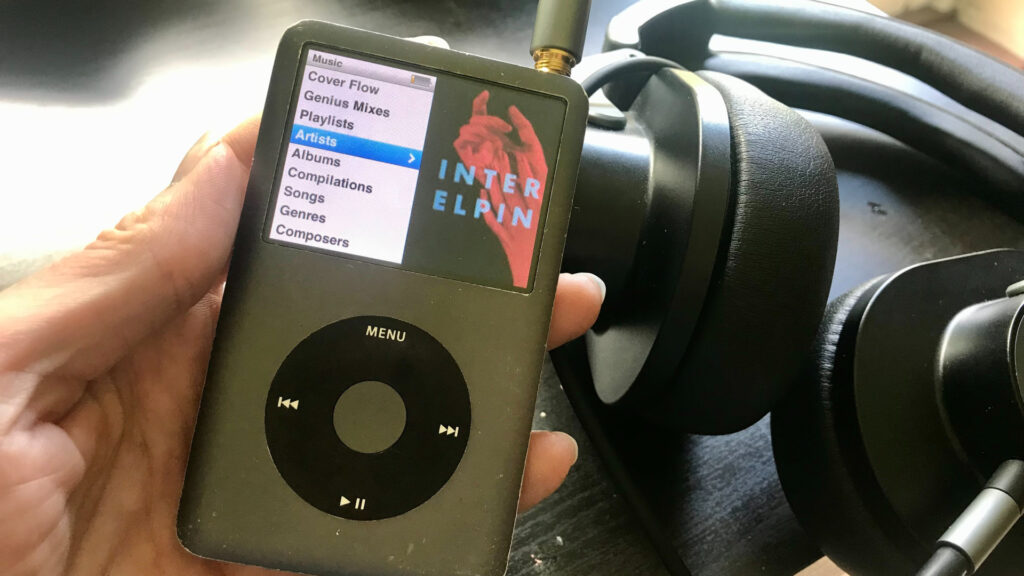
The iPod Era and Digital Music Players (2000s – Present):
Apple’s iPod, launched in 2001, revolutionized the way we consume and manage music. With its sleek design, intuitive interface, and massive storage capacity, the iPod became synonymous with portable music players. The integration of iTunes provided users with a seamless platform to purchase, organize, and sync their music libraries. The success of the iPod sparked fierce competition among tech companies, leading to the development of a myriad of digital music players and streaming services.
Pros
- Massive storage capacity for thousands of songs in a pocket-sized device.
- User-friendly interface for organizing and navigating music libraries.
- Seamless integration with digital music stores and online services.
Cons
- Dependency on battery life for playback.
- Risk of data loss or corruption without proper backup.
- Limited support for audio formats compared to other devices.
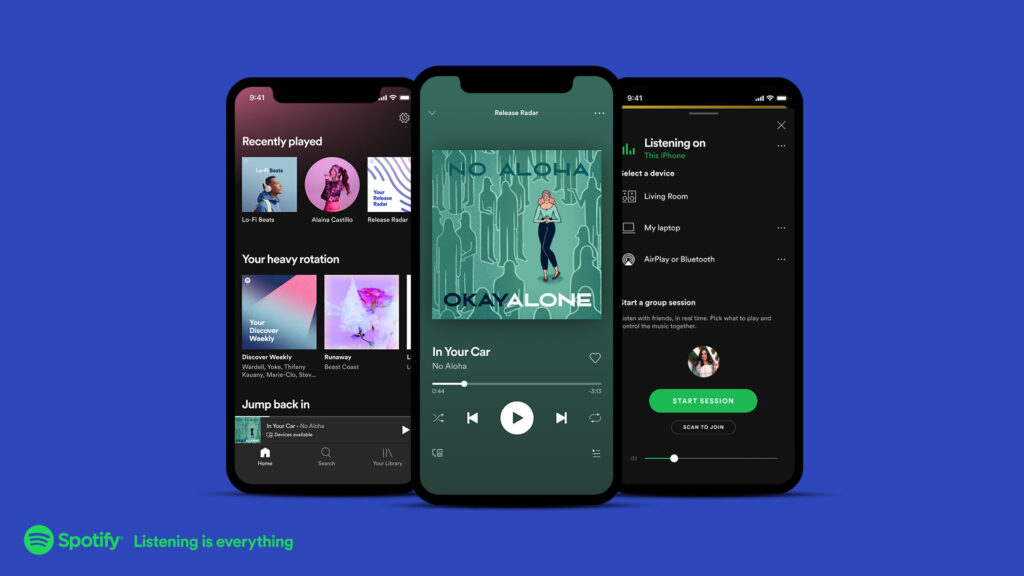
The Era of Streaming Services (2010s – Present):
The advent of high-speed internet and mobile technology heralded the rise of streaming services such as Spotify, Apple Music, and Tidal. Offering unlimited access to millions of songs on-demand, streaming platforms transformed the way we discover, share, and consume music. With personalized recommendations and curated playlists, users can explore a vast musical landscape tailored to their tastes. The convenience of streaming services has made owning physical music players obsolete for many, signaling a paradigm shift in music consumption habits.
Pros
- Unlimited access to vast libraries of music content.
- Personalized recommendations and curated playlists.
- Seamless streaming across multiple devices with internet connectivity.
Cons
- Reliance on a stable internet connection for uninterrupted playback.
- Loss of ownership and control over music files.
- Potential for subscription fees and data usage costs.
In conclusion, the evolution of music players has reached a point where it can be accessed anywhere in the world, there are no limitations with regards to geographical location, you can download music anytime and anywhere with the power of smartphones and the leverage of internet connectivity.