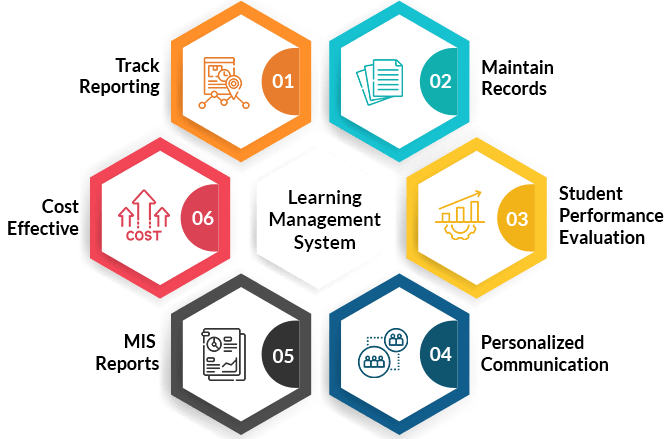
Learning Management Systems (LMS) are powerful tools that facilitate the delivery, management, and tracking of educational content. They are widely used in various settings, including schools, universities, corporations, and online learning platforms. Let’s explore what LMS are, how they are used, their benefits, drawbacks, and real-life applications.
What is an LMS?
An LMS is a software application or platform designed to manage and deliver educational content. It provides features for course creation, administration, tracking, and assessment.
Real-time Examples of Learning Management Systems (LMS):
- Schoology:
- Schoology is a robust LMS that supports remote learning models. It offers features for course creation, collaboration, and assessment.
- Masteriyo:
- Masteriyo is a comprehensive LMS known for its user-friendly interface and extensive course management capabilities.
- 360Learning:
- 360Learning is a collaborative LMS that empowers organizations to create, share, and improve training content together.
- Moodle:
- Moodle is an open-source LMS widely used in educational institutions and corporate environments. It offers customizable features for content delivery and assessment.
- Blackboard Learn:
- Blackboard Learn is a feature-rich LMS suitable for both academic and corporate training purposes. It provides tools for collaboration, content management, and compliance training.
- iSpring Learn:
- iSpring Learn is a cloud-based LMS focused on delivering interactive and engaging online courses. It offers features for multimedia content creation and tracking learner progress.
Applications and Usage:
- Education: LMS are used in schools and universities for online learning, course delivery, and student management.
- Corporate Training: Many businesses utilize LMS for employee onboarding, compliance training, and skill development.
- Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera and Udemy rely on LMS to deliver course content to learners globally.
Users:
- Teachers/Instructors: Create and deliver courses, and assess student performance.
- Students/Learners: Access course materials, and participate in activities and assessments.
- Administrators: Manage users, courses, and track progress.
Advantages:
- Accessibility: Learners can access content anytime, anywhere.
- Scalability: Can accommodate large numbers of users and courses.
- Tracking and Reporting: Detailed analytics help assess learner progress.
- Interactivity: Supports various multimedia formats for engaging learning experiences.
Disadvantages and Limitations:
- Cost: Implementation and maintenance can be expensive.
- Technical Issues: Requires reliable internet and technical support.
- Customization: Limited flexibility for customization in some platforms.
- Learning Curve: Users may require training to use the system effectively.
In conclusion, LMS plays a vital role in modern education and training environments. They offer numerous benefits but also come with challenges. Understanding their capabilities and limitations is essential for successful implementation and usage.