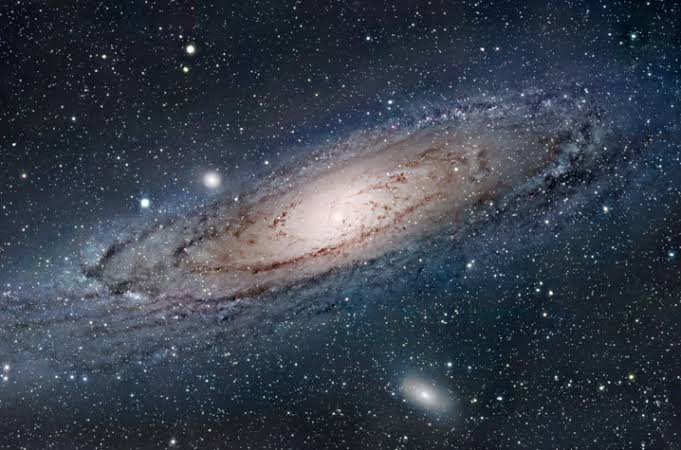
The Milky Way Galaxy, our cosmic home among billions of others, is a vast and awe-inspiring celestial realm that continues to captivate scientists and stargazers alike. Here are ten fascinating facts about the Milky Way that illuminate its beauty, complexity, and mysteries:
1. Galactic Size and Structure
The Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy, with a central bar-shaped structure surrounded by spiral arms extending outward. It spans an estimated diameter of 100,000 to 120,000 light-years, containing billions of stars, nebulae, and other celestial objects.
2. Galactic Population
Our galaxy is home to an estimated 100 to 400 billion stars, including our own Sun. Among these stars, astronomers have identified a diverse array of stellar types, from massive, luminous giants to small, dim dwarfs.
3. Spiral Arms
The Milky Way features several prominent spiral arms, including the Perseus Arm, Sagittarius Arm, and Orion Arm (where the Solar System resides). These arms are regions of dense interstellar gas and dust where new stars are born.
4. Galactic Center and Supermassive Black Hole
At the heart of the Milky Way lies a supermassive black hole called Sagittarius A*. This gravitational behemoth has a mass equivalent to about 4.3 million times that of the Sun and exerts a profound influence on the surrounding stars and gas clouds.
5. Galactic Rotation
Like a colossal cosmic carousel, the Milky Way rotates on its axis, with the Sun and the rest of the Solar System orbiting around the galactic center. It takes the Sun approximately 230 million years to complete one full revolution around the galaxy.
6. Galactic Cannibalism
The Milky Way has a history of galactic interactions and mergers with smaller satellite galaxies. Over billions of years, it has absorbed numerous dwarf galaxies, cannibalizing their stars, gas, and dust to grow in size and mass.
7. Dark Matter Halo
Surrounding the visible disk of the Milky Way is a vast halo of dark matter, an enigmatic substance that does not emit, absorb, or reflect light. Dark matter’s gravitational influence helps bind the galaxy together